Out with the Old: James Webb Telescope
What is the hype behind the new and mysterious James Webb Telescope?
What is the James Webb Telescope?
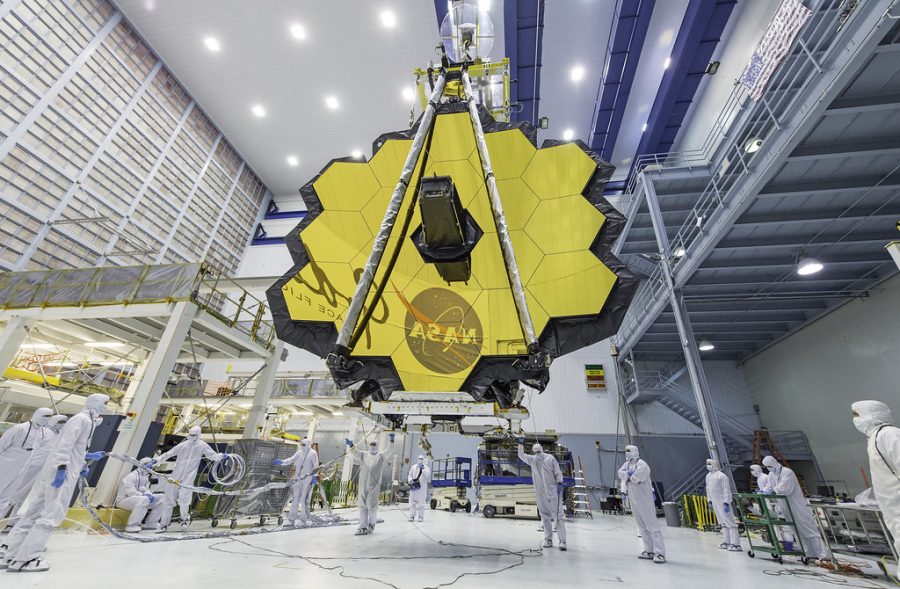
The James Webb Telescope has recently been spoken about all over the news, but what exactly is it and how does it work? To begin, the telescope is about as tall as a three-story building and as wide as a tennis court. Within it, eighteen pieces of mirror are puzzled together, which allows the telescope to see about thirteen point six billion light years away. This mechanic is what allows significant images to be taken. Outside light reflects on the mirrors, which then reflect onto distant objects, such as planets. The telescope is numerous years in the making and has many unique abilities, and is therefore unlike previous space gear. For example, the telescope is able to see through dust clouds using infrared lights, which gives scientists a glimpse of what was hiding behind them.
New Discoveries and Images
There have been many new discoveries made through the use of the James Webb Telescope, but one stands out: exoplanets. The newly accessible infrared lights incorporated into the telescope allows it to see the atmospheric composition of each planet. One example of the usage of this tool is on the exoplanet WASP-39, which was found to have an atmosphere containing carbon dioxide. This is significant because it is the first exoplanet discovered to have an atmosphere containing the element. Using the knowledge of a planet’s atmosphere gives light to the idea and the possible reality of other planets with the building blocks for life.
However, exoplanets aren’t the only discoveries made with this telescope–even some galaxies have been discovered. Due to the far vantage point of the tool, there are numerous galaxies scientists can see now, whether it was covered by dust clouds or previously too far away. The telescope has been able to capture photos of galaxies, which date back to around 300,000 million years after the Big Bang. In addition, galaxies formed soon after the Big Bang are able to be seen as they were over thirteen billion years ago. When it comes to galaxies, the telescope is able to see stars creating galaxies. They are pictured as faint, red dots in images of other space objects.
What Does This Mean For Oakton?
Evidently, a major change may be expected for the curriculum of future students. The telescope is discovering new objects, as well as furthering scientists’ understanding of certain galactical bodies at a rapid pace. What is to say there won’t be a huge discovery in the near future? Some ideas, such as older galaxies containing more distortion, have been proven to be false by the telescope. In addition to changes in curriculum, massive additions to it are expected as well, due to the pace of discovery. Not only will the understanding of astronomy be expanded, but some phenomena in other science topics, such as biology and physics, are plausible in the future as well.